Exploring the Boundaries of Virtual and Augmented Reality
The Evolution of Wearable Sensory Enhancement
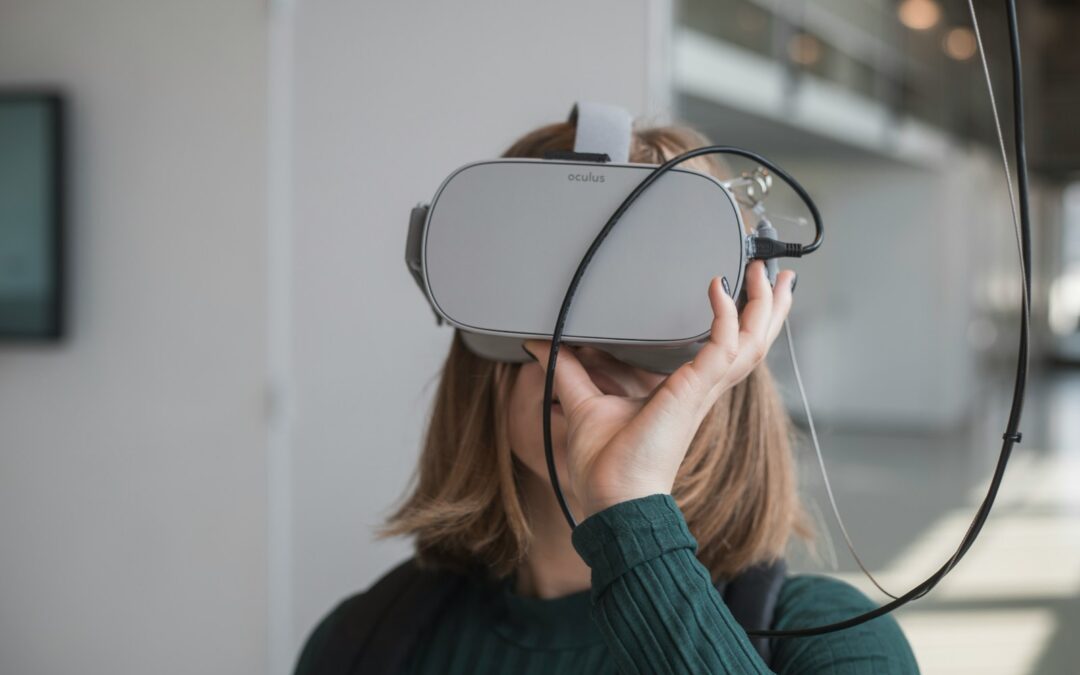
Wearable sensory enhancement in virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) represents a significant leap forward in immersive technology. This advancement has the potential to transform user experiences by providing more realistic and engaging interactions. In dynamic regions such as Saudi Arabia, UAE, Riyadh, and Dubai, where technology is rapidly evolving, the adoption of wearable sensory enhancement in VR and AR is poised to revolutionize various industries.
The concept of wearable sensory enhancement involves integrating devices that augment the senses, such as touch, smell, and even taste, into VR and AR systems. These enhancements allow users to experience a more lifelike and immersive environment. For example, haptic gloves can simulate the sensation of touch, providing feedback that mimics real-world interactions. This level of immersion can significantly enhance training simulations, gaming, and even virtual meetings.
In the context of VR and AR, sensory enhancement can also improve accessibility for individuals with disabilities. By providing sensory feedback that compensates for certain physical limitations, wearable devices can create inclusive experiences that cater to a wider audience. This inclusivity is particularly important in regions like Saudi Arabia and the UAE, where there is a strong emphasis on innovation and accessibility in technology.
Applications in Training and Education
One of the most promising applications of wearable sensory enhancement in VR and AR is in the field of training and education. In industries such as healthcare, aviation, and manufacturing, realistic training simulations are crucial for developing skills and ensuring safety. Wearable devices can provide trainees with tactile feedback, making virtual simulations feel more like real-life scenarios. This hands-on experience can improve learning outcomes and better prepare individuals for their roles.
In Saudi Arabia and Dubai, where there is a strong focus on technological innovation in education, the integration of wearable sensory enhancement into VR and AR can transform the learning experience. For example, medical students can practice surgical procedures with haptic feedback, allowing them to develop the necessary skills in a safe and controlled environment. Similarly, aviation trainees can use VR simulations with sensory enhancement to practice emergency procedures, ensuring they are well-prepared for real-world situations.
Moreover, the use of sensory-enhanced VR and AR in education extends beyond professional training. Schools and universities can leverage this technology to create more engaging and interactive learning experiences. By simulating historical events or scientific phenomena with sensory feedback, educators can make abstract concepts more tangible and understandable for students. This approach can enhance retention and make learning more enjoyable.
Enhancing Customer Experiences in Retail and Entertainment
The retail and entertainment industries are also set to benefit significantly from wearable sensory enhancement in VR and AR. In retail, sensory-enhanced VR can create immersive shopping experiences that allow customers to try products before making a purchase. For instance, a customer can virtually try on clothes with haptic feedback that simulates the texture and fit of the fabric. This level of interaction can enhance customer satisfaction and reduce return rates.
In entertainment, wearable sensory enhancement can take VR gaming and experiences to new heights. By incorporating sensory feedback, game developers can create more immersive and engaging environments. Players can feel the impact of in-game actions, such as the recoil of a virtual weapon or the texture of virtual objects. This added layer of realism can make VR games more captivating and enjoyable.
Dubai and Riyadh, known for their vibrant entertainment and retail sectors, are well-positioned to lead the adoption of this technology. By integrating wearable sensory enhancement into their VR and AR offerings, businesses in these cities can attract tech-savvy customers looking for innovative and immersive experiences. This competitive edge can drive growth and establish these regions as leaders in cutting-edge technology.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Addressing Technological and Ethical Challenges
While the potential of wearable sensory enhancement in VR and AR is immense, several challenges need to be addressed to realize its full potential. Technologically, creating realistic and reliable sensory feedback devices requires significant research and development. Ensuring that these devices are comfortable and accessible for prolonged use is also crucial. Companies in Saudi Arabia and the UAE are investing heavily in R&D to overcome these challenges and develop world-class solutions.
Ethically, the integration of sensory enhancement raises questions about user privacy and data security. Wearable devices collect a vast amount of data about user interactions, which must be protected from misuse. Developers and policymakers need to establish robust data protection frameworks to safeguard user privacy. Additionally, the potential for addiction and over-reliance on immersive technologies must be considered, with measures put in place to promote healthy usage habits.
Collaborative Learning and Business Success
The integration of wearable sensory enhancement in VR and AR also has implications for collaborative learning and business success. In the context of executive coaching and leadership training, sensory-enhanced VR can provide realistic scenarios that help leaders develop critical skills. By simulating high-pressure situations with sensory feedback, executives can practice decision-making and crisis management in a controlled environment. This experiential learning approach can lead to more effective and confident leaders.
In the business sector, companies can use sensory-enhanced VR for team-building exercises and remote collaboration. By creating virtual environments where employees can interact and collaborate with sensory feedback, businesses can foster a sense of presence and engagement. This approach is particularly valuable for remote teams, enabling them to work together effectively despite geographical distances. In regions like Riyadh and Dubai, where international business is thriving, such technologies can enhance productivity and innovation.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Immersive Technology
The potential applications of wearable sensory enhancement in virtual and augmented reality are vast and varied. From transforming training and education to revolutionizing retail and entertainment, this technology holds the promise of creating more immersive and engaging experiences. In regions like Saudi Arabia, UAE, Riyadh, and Dubai, the adoption of wearable sensory enhancement is set to drive innovation and set new standards in various industries.
As we move forward, it is essential to address the technological and ethical challenges associated with this technology. By prioritizing research and development, ensuring data security, and promoting responsible usage, we can harness the full potential of wearable sensory enhancement in VR and AR. Embracing these advancements will not only enhance user experiences but also contribute to business success and societal progress.
#WearableTechnology #SensoryEnhancement #VirtualReality #AugmentedReality #SaudiArabia #UAE #Riyadh #Dubai #AI #Blockchain #ModernTechnology #ExecutiveCoaching #BusinessSuccess